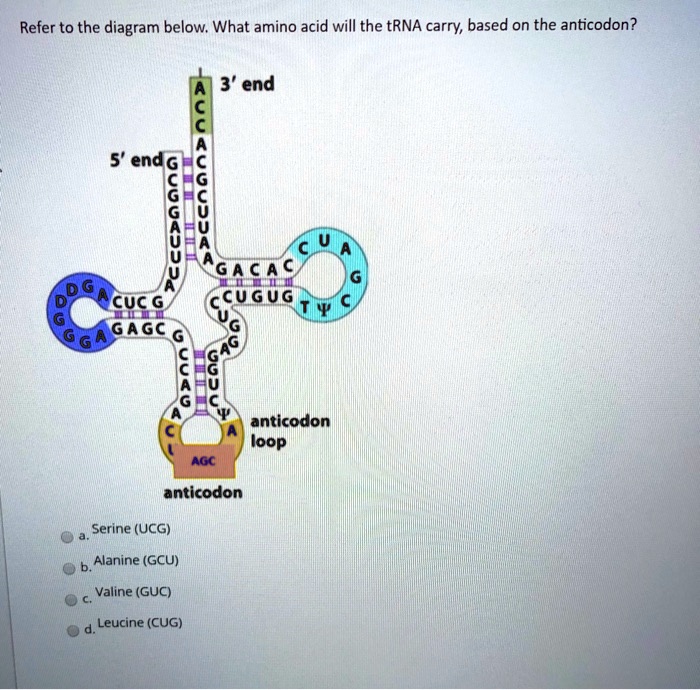
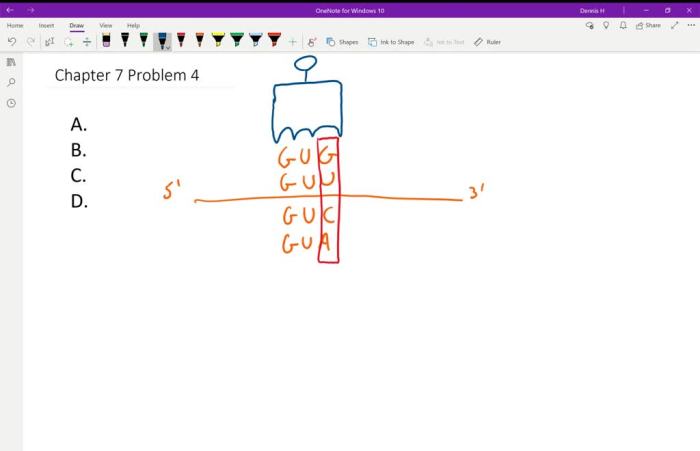
Refer to the table the anticodon for valine is 3′-UAC-5′. This sequence plays a crucial role in protein synthesis, ensuring the accurate translation of genetic information. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of codons, anticodons, and their significance in the intricate process of life.
The genetic code, a universal language of life, governs the synthesis of proteins, the building blocks of our cells. Within this code, codons, triplets of nucleotides, specify each amino acid. Anticodons, carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), are complementary to codons, ensuring precise recognition and incorporation of amino acids into the growing polypeptide chain.
The anticodon for valine, 3′-UAC-5′, pairs with the codon 5′-GUA-3′, facilitating the incorporation of valine into proteins.
Introduction to the Genetic Code: Refer To The Table The Anticodon For Valine Is
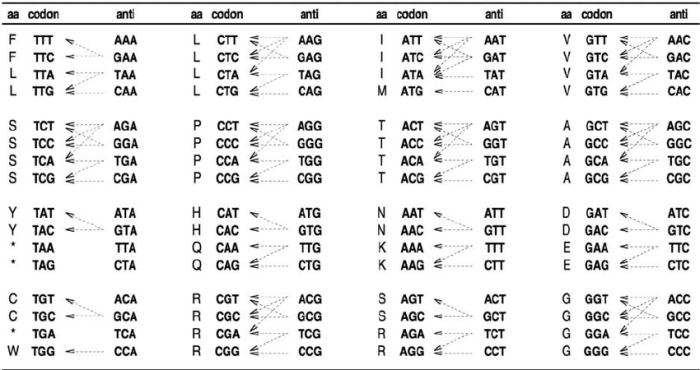
The genetic code is a set of rules that determines how the information encoded in DNA and RNA is translated into proteins. It is a universal code that is shared by all living organisms. The genetic code is read in groups of three nucleotides, called codons.
Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal.
Anticodons are complementary sequences of three nucleotides that are found on tRNA molecules. They recognize and bind to codons on mRNA molecules, ensuring that the correct amino acids are added to the growing polypeptide chain during protein synthesis.
The Anticodon for Valine
The anticodon for valine is 3′-UAC-5′. It is complementary to the codon for valine, which is 5′-GUA-3′. This complementarity is essential for accurate protein synthesis. If the anticodon did not match the codon, the wrong amino acid would be added to the polypeptide chain.
Table of Codons and Anticodons
| Amino Acid | Codon | Anticodon |
|---|---|---|
| Valine | 5′-GUA-3′ | 3′-UAC-5′ |
| Alanine | 5′-GCA-3′ | 3′-CGU-5′ |
| Serine | 5′-UCA-3′ | 3′-AGU-5′ |
| Leucine | 5′-CUA-3′ | 3′-GAU-5′ |
Methods for Determining the Anticodon for Valine, Refer to the table the anticodon for valine is
The anticodon for valine was determined using a combination of experimental methods, including:
- In vitro translation assays
- Genetic engineering techniques
These methods allowed researchers to identify the specific tRNA molecule that recognizes the codon for valine and to determine its anticodon sequence.
Applications of Anticodon Knowledge
Knowing the anticodon for valine has a number of applications, including:
- Biotechnology and genetic engineering:Anticodon knowledge can be used to design synthetic tRNA molecules that can be used to insert specific amino acids into proteins.
- Medical diagnostics:Anticodon knowledge can be used to develop diagnostic tests for genetic diseases that are caused by mutations in tRNA molecules.
- Evolutionary biology:Anticodon knowledge can be used to study the evolution of the genetic code.
Top FAQs
What is the anticodon for valine?
The anticodon for valine is 3′-UAC-5′.
How does the anticodon for valine ensure accurate protein synthesis?
The anticodon for valine is complementary to the codon for valine (5′-GUA-3′), ensuring that the correct amino acid (valine) is incorporated into the growing polypeptide chain.
What are the applications of knowing the anticodon for valine?
Knowing the anticodon for valine has applications in biotechnology, genetic engineering, medical diagnostics, and evolutionary biology.